生命周期是一定要知道的,这样才知道整个组件的工作流程,知道哪些操作适合在哪个回调中进行……(o^^o)
一个栗子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
| import React, {Component} from 'react';
import {
View,
Text,
StyleSheet,
} from 'react-native';
export default class App extends Component<Props> {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
console.log('constructor')
this.state = {
result: '点击前',
};
}
componentWillMount() {
console.log('componentWillMount')
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount')
}
componentWillReceiveProps() {
console.log('componentWillReceiveProps')
}
shouldComponentUpdate() {
console.log('shouldComponentUpdate')
return true;
}
componentDidUpdate() {
console.log('componentDidUpdate')
}
componentDidMount() {
console.log('componentDidMount')
}
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('componentWillUnmount')
}
componentWillUpdate() {
console.log('componentWillUpdate')
}
render() {
console.log('render')
return (
<View style={styles.content}>
<Text style={styles.text} onPress={
() => {
this.setState({
result: '点击后'
})
}
}>
{this.state.result}
</Text>
</View>
)
}
}
const styles = StyleSheet.create({
content: {
flex: 1,
justifyContent: 'center',
alignItems: 'center',
},
text: {
padding: 50,
fontSize: 20,
color: '#ffffff',
backgroundColor: '#00a056'
}
})
|
console
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| constructor
App.js:39 componentWillMount
App.js:103 render
App.js:86 componentDidMount
App.js:108 onPress call
App.js:66 shouldComponentUpdate
App.js:100 componentWillUpdate
App.js:103 render
App.js:76 componentDidUpdate
|
组件的生命周期
通过上面的栗子,有灵性的小哥哥已经基本猜到大致的生命周期了
下面再看看这张我偷来的帅图
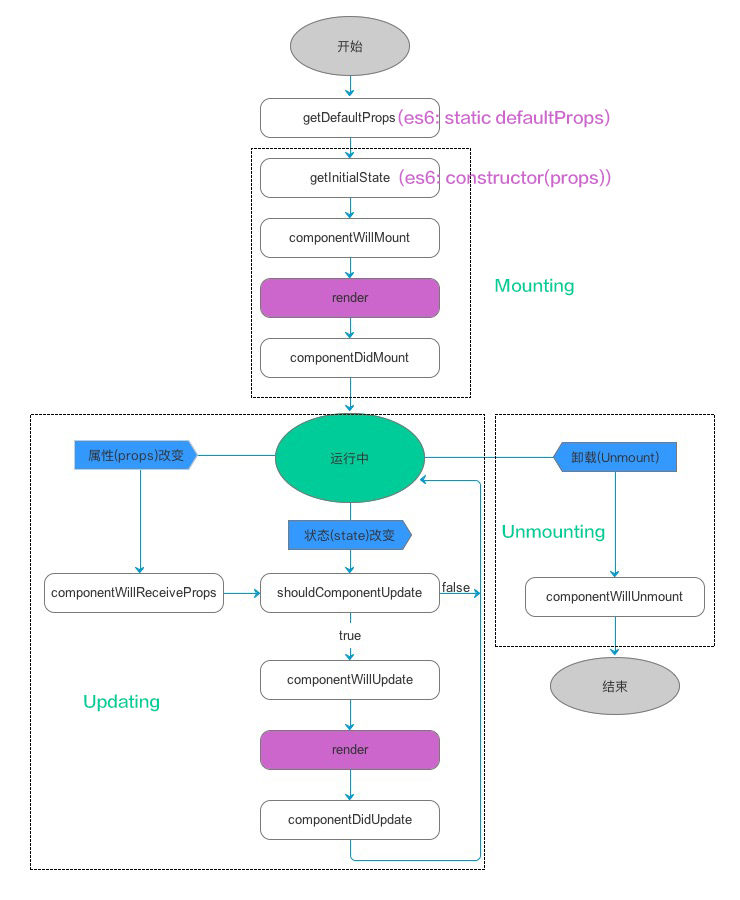
再结合这张酷表
| 生命周期 |
调用次数 |
能否使用 setSate() |
描述 |
| getDefaultProps(es6:static defaultProps) |
1(全局调用一次) |
否 |
初始化默认属性 |
| getInitialState(es6:constructor(props)) |
1 |
否 |
构造函数,初始化需要的state |
| componentWillMount |
1 |
是 |
控件渲染前触发 |
| render |
>=1 |
否 |
渲染控件的方法 |
| componentDidMount |
1 |
是 |
控件渲染后触发 |
| componentWillReceiveProps |
>=0 |
是 |
组件接收到新的props时被调用 |
| shouldComponentUpdate |
>=0 |
否 |
当组件接收到新的props和state时被调用 |
| componentWillUpdate |
>=0 |
否 |
props或者state改变,并且此前的shouldComponentUpdate方法返回为 true会调用该方法 |
| componentDidUpdate |
>=0 |
否 |
组件重新渲染完成后会调用此方法 |
另外还有一个场景需要知道的,代码我就不贴了
父组件中有一个子组件,点击父组件调用setState,那么父子组件的生命周期如何回调?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
constructor
App.js:42 componentWillMount
App.js:107 render
ChildComponent.js:26 ChildComponent,constructor
ChildComponent.js:41 ChildComponent,componentWillMount
ChildComponent.js:106 ChildComponent,render
ChildComponent.js:88 ChildComponent,componentDidMount
App.js:89 componentDidMount
shouldComponentUpdate
App.js:103 componentWillUpdate
App.js:107 render
ChildComponent.js:59 ChildComponent,componentWillReceiveProps
ChildComponent.js:68 ChildComponent,shouldComponentUpdate
ChildComponent.js:102 ChildComponent,componentWillUpdate
ChildComponent.js:106 ChildComponent,render
ChildComponent.js:78 ChildComponent,componentDidUpdate
App.js:79 componentDidUpdate
|
可以看到:
- 组件的加载是从内到外一级一级的,这个和android类似
- 修改父组件state,触发update整个流程,但是不再次触发子组件的constructor
推荐的操作
- constructor()方法里初始化state
- static defaultProps指定默认属性
- componentDidMount():该方法在render()方法后自动调用,网络请求一般放在这个方法中
- shouldComponentUpdate():该方法返回一个boolean值,用来决定是否需要重新渲染组件,默认返回true,你可以自己重写此方法,通过条件判断来决定你是否需要更新组件
- componentWillUnmount():在组件被移除前调用,在该方法中,释放一些不需要的资源,比如停止定时器
- 不要在 constructor 或者 render 里 setState()
- constructor 已含 this.state={}
- render 里 setState 会造成setState -> render -> setState -> render
- 能做的setState,只要是render前,就放在componentWillMount,render后,就放在 componentDidMount。這两个 function 是 react lifecycle 中,最常使用的两个
- 更多以后再添加总结
补充
关于componentWillReceiveProps
componentWillReceiveProps:是在组件的props的更新的时,调用,那么有人就会有疑惑,组件的props不是不能改变的吗,只有state是可以改变的。注意,props确实不能修改的,指的是不能被自己修改,props是父组件传入进来的,在父组件首次render的时候,该方法不会被调用,那么由于父组件的State改变,render重新调用,传入子组件的props跟上次不同,那么这个方法就会被调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<View style={{marginTop: 15}}>
<CommonButton {...this.button} text={this.state.username} onPressFunc={this._onLogin}/>
</View>
//以下是子组件-CommonButton
//componentWillReceiveProps方法,在父组件,多次render会调用,我们一半先判断一下,和上次的是否相同,
//如果不相同,就设置子组件的state,让其更新
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
if(nextProps.text!==this.props.text){
this.setState({
text: nextProps.text
})
}
}
|
参考
React-Native生命周期的触发场景和一些小建议
React Native 中组件的生命周期
React Native之React速学教程(中)/)
